Indicator Gauge Icon Legend
Legend Colors
Red is bad, green is good, blue is not statistically different/neutral.
Compared to Distribution
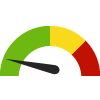 the value is in the best half of communities.
the value is in the best half of communities.
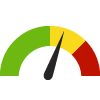 the value is in the 2nd worst quarter of communities.
the value is in the 2nd worst quarter of communities.
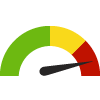 the value is in the worst quarter of communities.
the value is in the worst quarter of communities.
Compared to Target
 meets target;
meets target;  does not meet target.
does not meet target.
Compared to a Single Value
 lower than the comparison value;
lower than the comparison value;
 higher than the comparison value;
higher than the comparison value;
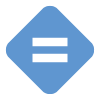 not statistically different from comparison value.
not statistically different from comparison value.
Trend

 non-significant change over time;
non-significant change over time; 
 significant change over time;
significant change over time; 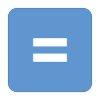 no change over time.
no change over time.
Compared to Prior Value
 higher than the previous measurement period;
higher than the previous measurement period;
 lower than the previous measurement period;
lower than the previous measurement period;
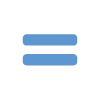 no statistically different change from previous measurement period.
no statistically different change from previous measurement period.
 Significantly better than the overall value
Significantly better than the overall value
 Significantly worse than the overall value
Significantly worse than the overall value
 No significant difference with the overall value
No significant difference with the overall value
 No data on significance available
No data on significance available
Colorectal Cancer Mortality Rate
This indicator is archived and is no longer being updated. Click to learn more
Colorectal cancer mortality rate (crude) per 100,000 population.
Why is this important?
-
Among cancers impacting both men and women, colorectal cancer is the second highest cause of cancer-specific deaths in the United States. Age is a contributing factor to increased risk for colon and rectal cancers. Other risk factors include family history, colorectal polyps, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, lack of physical activity, low fruit and vegetable consumption, diet low in fiber and high in fat, being overweight or obese, alcohol consumption and tobacco use.
Regular and timely screenings are designed to catch the disease in an early stage when it may be halted or even fully reversed with treatment. The US Preventative Service Taskforces (USPSTF) recommends screening for colorectal cancer starting at age 50, including an annual fecal immunochemical test (FIT), which identifies blood in stool, and sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy, every 10 years unless an irregular test result occurs.
Measurement period: 2022
Maintained by: Truckee Meadows Tomorrow
Last update: July 2024
Graph Selections
Data Source
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Note: This source uses Zip Code Tabulation Areas (ZCTAs) for its Zip Code data. Learn more
Maintained By: Truckee Meadows Tomorrow
Filed under: Health / Mortality Data, Health / Cancer, Health Outcomes